Blood Thinners: What They Are, How They Interact, and What You Need to Know
When you take a blood thinner, a medication that reduces your blood’s ability to clot. Also known as anticoagulants, it’s not about making your blood watery—it’s about stopping dangerous clots before they cause strokes, heart attacks, or pulmonary embolisms. Millions rely on these drugs every day, especially after stents, atrial fibrillation, or deep vein thrombosis. But here’s the catch: blood thinners don’t play nice with a lot of other things you might be taking.
That’s why drug interactions, when one medicine changes how another works. Also known as medication conflicts, they’re behind many hospital visits involving blood thinners. Take trimethoprim, a common antibiotic—it can spike potassium levels and make your heart rhythm unstable if you’re also on a blood thinner. Or NSAIDs like ibuprofen: they increase bleeding risk and can wreck your stomach lining when combined with warfarin or apixaban. Even something as simple as a protein shake can interfere with how your body absorbs thyroid meds, which might indirectly affect your clotting if you’re on multiple prescriptions.
And it’s not just about other pills. Your liver health matters. If you have cirrhosis, your body can’t break down blood thinners the way it should—leading to dangerous buildup. Same with kidney function: some newer blood thinners rely on your kidneys to clear them out. If those organs aren’t working right, the dose needs to change. That’s why doctors check liver scores like Child-Pugh or kidney markers before prescribing. And don’t forget about diet. Vitamin K in leafy greens can undo warfarin’s effect. One week you eat salads, next week you don’t—your INR swings, and suddenly you’re at risk.
These aren’t theoretical risks. Real people get hurt because they didn’t know their painkiller, antibiotic, or supplement was playing hide-and-seek with their blood thinner. That’s why post-market surveillance matters—clinical trials miss these clashes because they’re too small and too short. The real world is messier, and that’s where the danger hides.
Below, you’ll find real-world stories and hard facts about how blood thinners behave when mixed with other conditions, meds, and habits. From how to store your prescription labels to avoid mix-ups, to why certain antibiotics raise bleeding risk, to what happens when your liver can’t keep up—this collection gives you the practical details you won’t get from a pamphlet. No fluff. No guesswork. Just what you need to stay safe.
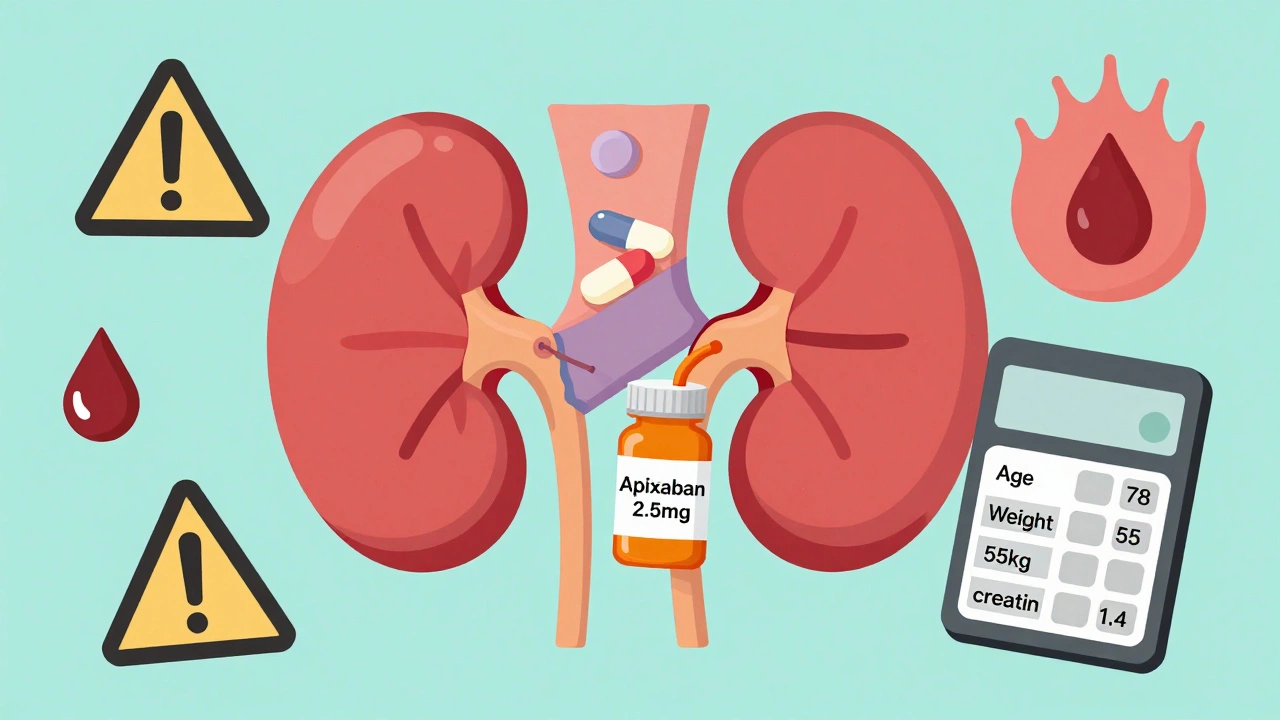
DOACs in Renal Impairment: How to Adjust Doses to Prevent Bleeding and Clots
- Dec, 1 2025
- 13
DOACs like apixaban and rivaroxaban are common blood thinners, but kidney problems require precise dose adjustments to prevent bleeding or clots. Learn the rules for safe use.
Categories
- Medication Information (113)
- Health and Wellness (52)
- Women's Health (6)
- Support Resources (5)
- Supplements (5)
- Pharmacy Reviews (5)
- Dermatology (4)
- Mental Health (4)
- Nutrition (3)
- Fitness and Wellness (3)
Archives
- February 2026 (12)
- January 2026 (27)
- December 2025 (30)
- November 2025 (24)
- October 2025 (29)
- September 2025 (14)
- August 2025 (2)
- July 2025 (7)
- June 2025 (2)
- May 2025 (3)
- April 2025 (4)
- March 2025 (3)
- online pharmacy
- dietary supplement
- medication safety
- health benefits
- side effects
- generic drugs
- drug interactions
- treatment
- wellness
- optimal health
- diabetes management
- safe medication purchase
- online pharmacy Australia
- brand name drugs
- authorized generics
- generic medications
- link
- women's health
- dietary supplements
- sleep
